Create Excel Files With Python
First we are going to create a csv file using the build-in csv module, after that we will proceed to use a third party library to create a xlsx file.
Creating a CSV file
To be able to work with this type of file we are going to import CSV in the following way
CVS Module
the CVS module includes all necessary methods built-in some of which are:
- csv.reader
- csv.writer
- csv.DictReader
- csv.DictWriter
with this method we can edit, modify and manipulate the stored data in a csv file.
Initial preparation
First we will need to prepare the file so it can be run with python namefile.py for that we add the if __name__ == "__main__"
| import csv
if __name__ = "__main__":
main()
|
Name of the file, header and data
Now, we proceed to define some variables, the name of the file with filename, later the headers ( or the name of the columns) with header and provide some data with data
| import csv
filename = "imdb_top_4.csv"
header = ("Rank", "Rating", "Title")
data = [
(1, 9.2, "The Shawshank Redemption(1994)"),
(2, 9.2, "The Godfather(1972)"),
(3, 9, "The Godfather: Part II(1974)"),
(4, 8.9, "Pulp Fiction(1994)")
]
if __name__ = "__main__":
main()
|
Function to write on the file
The next step will be create a function that write the data on the file,
this function will have 3 parameters, header,data, and filename.
Inside this function we will write the first line of the file with the content of header, this will give the name to the columns and later with a for loop we will write the data.
| def writer(header,data,filename):
with open(filename,"w",newline = " ") as csvfile:
movies = cvs.writer(csvfile)
movies.writerow(header)
for x in data:
movies.writerow(x)
|
so the full, first version of the script will be, notice that there is a call to the function writer after the variable data is defined.
| import csv
filename = "imdb_top_4.csv"
header = ("Rank", "Rating", "Title")
data = [
(1, 9.2, "The Shawshank Redemption(1994)"),
(2, 9.2, "The Godfather(1972)"),
(3, 9, "The Godfather: Part II(1974)"),
(4, 8.9, "Pulp Fiction(1994)")
]
writer(header, data, filename, "write")
def writer(header,data,filename):
with open(filename,"w",newline = " ") as csvfile:
movies = cvs.writer(csvfile)
movies.writerow(header)
for x in data:
movies.writerow(x)
if __name__ = "__main__":
main()
|
And the result will be like:
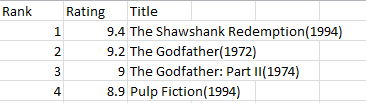
Updating a CSV files
To update this type of file and in this case we will need to create a new function named 'updater' that will just take the filename as a parameter.
| def updater(filename):
with open(filename, newline= "") as file:
readData = [row for row in csv.DictReader(file)]
readData[0]['Rating'] = '9.4'
readHeader = readData[0].keys()
writer(readHeader,readData,filename,"update")
|
In this function:
- We open the file define in
filename and we are going to called it 'file'.
- Save all the information from that file in a variable called
readData, cvs.DictReader
- the next line
readData[0]['Rating'] = '9.4' is hard-coding the value 9.4 in the 'Rating' column.
- the last line will tell the function
writer that we are executing an update ( this option is not yet define in the function writer that will be the next step)
- finally we add a call to the function
uodater after the call to the function writer
| import csv
filename = "imdb_top_4.csv"
header = ("Rank", "Rating", "Title")
data = [
(1, 9.2, "The Shawshank Redemption(1994)"),
(2, 9.2, "The Godfather(1972)"),
(3, 9, "The Godfather: Part II(1974)"),
(4, 8.9, "Pulp Fiction(1994)")
]
writer(header, data, filename, "write")
updater(filename)
def writer(header,data,filename):
with open(filename,"w",newline = " ") as csvfile:
movies = cvs.writer(csvfile)
movies.writerow(header)
for x in data:
movies.writerow(x)
# TODO option to update
def updater(filename):
with open(filename, newline= "") as file:
readData = [row for row in csv.DictReader(file)]
readData[0]['Rating'] = '9.4'
readHeader = readData[0].keys()
writer(readHeader,readData,filename,"update")
if __name__ = "__main__":
main()
|
Create the option for update
Now, we need to modify the function writer to be able to receive an extra parameter, and inside, some modifications to handle these options for "write"
and "update".
- lets add the extra parameter, this will be called option
| def writer(header, data, filename, option):
...
|
- Inside we are going to create a decision loop to execute some part of the code depending of the the parameter option
| def writer(header, data, filename, option):
with open(filename, "w", newline = "") as csvfile:
if option == "write":
movies = csv.writer(csvfile)
movies.writerow(headers)
for x in data:
movies.writerow(x)
elif option == "update":
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames = headers)
writer.writeheader()
write.writerow(data)
else:
print("option is not know")
|
More information about DictWriter here but basically here is use to write a row with the field names.
so with all this changes we will have a script that look like this:
| import csv
filename = "imdb_top_4.csv"
header = ("Rank", "Rating", "Title")
data = [
(1, 9.2, "The Shawshank Redemption(1994)"),
(2, 9.2, "The Godfather(1972)"),
(3, 9, "The Godfather: Part II(1974)"),
(4, 8.9, "Pulp Fiction(1994)")
]
writer(header, data, filename, "write")
updater(filename)
def writer(header, data, filename, option):
with open(filename, "w", newline = "") as csvfile:
if option == "write":
movies = csv.writer(csvfile)
movies.writerow(headers)
for x in data:
movies.writerow(x)
elif option == "update":
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames = headers)
writer.writeheader()
write.writerow(data)
else:
print("option is not know")
def updater(filename):
with open(filename, newline= "") as file:
readData = [row for row in csv.DictReader(file)]
readData[0]['Rating'] = '9.4'
readHeader = readData[0].keys()
writer(readHeader,readData,filename,"update")
if __name__ = "__main__":
main()
|
The xlsx File
This will be an enhancement of the previous part, that doesn't mean previous part is not a solution, just that this solution will include openpyxl which is a all in one solution to work with worksheets, loading, updating m renaming and deleting them.
Basic terminology
- WorkBook is the name for a an Excel file in
openpyxl.
- A workbook consist of sheets( default is 1 sheet). sheets are referenced by their names.
- A Sheet consist of rows ( horizontal lines) starting from the number 1 and columns ( vertical lines) starting the letter A.
- Rows and columns result in a grid and form cells which may contain some data ( numerical or string value) or formulas.
First Steps with openpyxl
First we need to install openpyxl this can be done using pip
For the most basic usage, this been creating a new workbook with just one sheet
Create a workbook
To create a workbook we can use the function Workbook()
| from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
|
| from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active
|
by default the name of the sheet will be "sheet" and a number, so the first sheet will be "sheet", the second "Sheet1", etc.
Now, we have the workbook and the first sheet, what about the second sheet?, To create the second sheet and all the following sheets, we use create_sheet("name of the sheet")
| from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active
ws1 = wb.create_sheet("second sheet")
|
We can use the create_sheet("name of the sheet") and by defautl the sheet will be created after the previous sheet, but if we want to insert the sheet in a specific spot we can use create_sheet("name of the sheet",0) in this case this sheet will be insert in the first spot.
At any moment we can change the title of the sheet using .title as follow
| from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active
ws1 = wb.create_sheet("second sheet")
#change the name of the first sheet
ws.title = "first sheet"
|
Save the workbook
To save the workbook, first we need to give it a name dest_filename = "name of the file", later, we use the function save(filename="name of the workbook")
| from openpyxl import Workbook
# Creating the workbook
wb = Workbook()
# the name of the file
dest_filename = 'test_openpyxl.xlsx'
ws = wb.active
ws1 = wb.create_sheet("second sheet")
#change the name of the first sheet
ws.title = "first sheet"
wb.save(filename = dest_filename)
|
For more details or tutorial we can visit openpyxl documentation
we just saw how to create a workbook, now, for this example, we are going to focus in manipulate a workbook that already exist, for that reason we will create one called "Customers1.xlsx" and continue working on it
Working with xlsx files
Now, we are going to work with an existing file called "customers1.xlsx", this look like this:
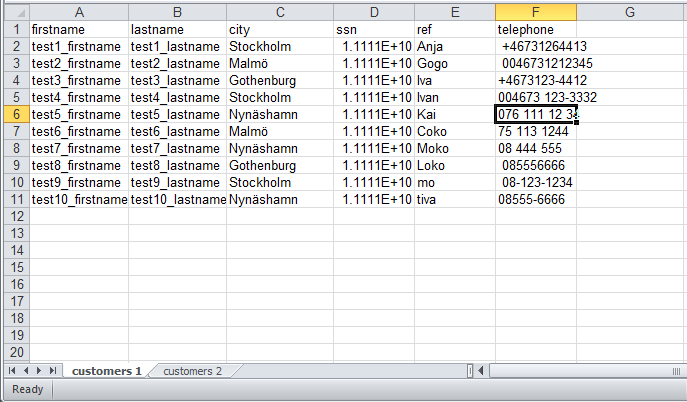
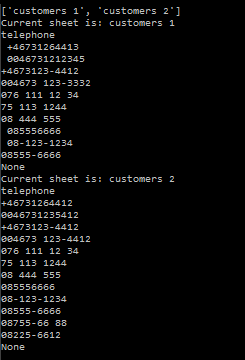
The file contain 6 columns and 11 rows, We are going to import it and:
- Print the sheets name
- save the current sheet on the variable
current_Sheet
- print the value of the second column and 4 row (B4).
| import openpyxl as opxl
theFile = opxl.load_workbook('Customers1.xlsx')
print(theFile.sheetnames)
|

We got the file, and display the sheets names, now step 2 and 3, Save the current sheet in a variable and print the value of the cell B4.
| import openpyxl as opxl
theFile = opxl.load_workbook('Customers1.xlsx')
print(theFile.sheetnames)
current_sheet = theFile['customers 1']
print(current_sheet['B4'].value)
|
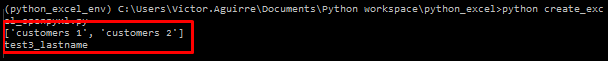
there is hardcoded values in this script which make it not that flexible, but we can make modifications in the future, for now we are going to do the following:
- Read the file
- Get all sheet names
- Loop through all sheets
- In the last step, the code will print values that are located in B4 fields of each found sheet inside the workbook.
| import openpyxl as opxl
the_File = opxl.load_workbook('Customers1.xlsx')
print(the_File.sheetnames)
all_sheets = the_File.sheetnames
for x in all_sheets:
current_sheet = the_File[x]
print(current_sheet['B4'].value)
|
Next, We will use the string 'ABCDEF' to create a loop through the content of each sheet.
| import openpyxl as opxl
the_File = opxl.load_workbook('Customers1.xlsx')
print(the_File.sheetnames)
columns_marks = 'ABCDEF'
all_sheets = the_File.sheetnames
for x in all_sheets:
current_sheet = the_File[x]
for row in range(1, current_sheet.max_row + 1):
for column in columns_marks:
cell_name = "{}{}".format(column, row) # creat the structure B4 or C4 etc
print("Cell Position: {} has the value {}".format(cell_name,current_sheet[cell_name].value))
|
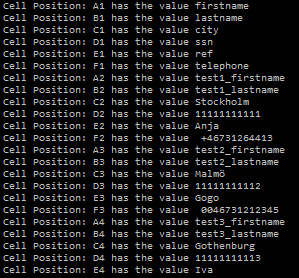
Rudimentary way to find content of a column
The idea will be find the content of the column named "telephone" and display its content.
For that we will start by creating a function that will hold the loops, this loops will look row by row and column by column until we found the column named "telephone"
| def find_specific_cell():
for row in range(1, current_sheet.max_row + 1):
for column in columns_marks:
cell_name = "{}{}".format(column,row)
if current_sheet[cell_name].value == "telephone":
return cell_name
|
now with the function, we can create a loop that iterate over the different sheets looking for the specific column that we are looking for
| for sheet in all_sheets:
current_sheet = the_File[sheet]
print(find_specific_cell)
|
so the script including this new function will be:
| import openpyxl as opxl
the_File = opxl.load_workbook('Customers1.xlsx')
print(the_File.sheetnames)
columns_marks = 'ABCDEF'
all_sheets = the_File.sheetnames
def find_specific_cell():
for row in range(1, current_sheet.max_row + 1):
for column in columns_marks:
cell_name = "{}{}".format(column, row) # create the structure B4 or C4 etc
if current_sheet[cell_name].value == "telephone":
return cell_name
for sheet in all_sheets:
print("Current sheet is: {}".format(sheet))
current_sheet = the_File[sheet]
print(find_specific_cell())
|
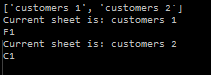
so, with few modification and the creation of the second functions we have
| import openpyxl as opxl
the_File = opxl.load_workbook('Customers1.xlsx')
print(the_File.sheetnames)
columns_marks = 'ABCDEF'
#adding all the sheets to this variable
all_sheets = the_File.sheetnames
def find_specific_cell():
for row in range(1, current_sheet.max_row + 1):
for column in columns_marks:
cell_name = "{}{}".format(column, row)
if current_sheet[cell_name].value == "telephone":
return (cell_name,column)
def print_all(cell_name):
_ , column_letter = cell_name
for row in range(1, current_sheet.max_row +1):
cell = column_letter + str(row)
print(current_sheet[cell].value)
for sheet in all_sheets:
print("Current sheet is: {}".format(sheet))
current_sheet = the_File[sheet]
cell = find_specific_cell()
print(print_all(cell))
|