Visualization Crash course
Here we mentioned the very basics for the visualization tools, just enough to understand how Pandas plotting and Seaborn are built on top of Matplotlib.
Matplotlib¶
It is common to create an alias for Matplotlib as plt and that will in this way:
Now, since Jupyter notebooks is the most common tool it is important to mentione that we need to add an extra line after importing matplotlib.pyplot. so a common import session of a file will look like:
Simple plot¶
To simple plot we can use plot(x,y) but in jupyter notbooks we can add a ";" at the end so the matplotlib text wont be display
in a .py file we will need to add
plt.show()in order to see the graph
we will create a DataFrame that we can use to plot
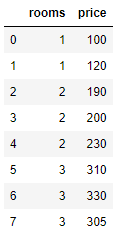
If we use the normal plot this will display some straight line but if we use the scatter we will have dots in the x and Y points
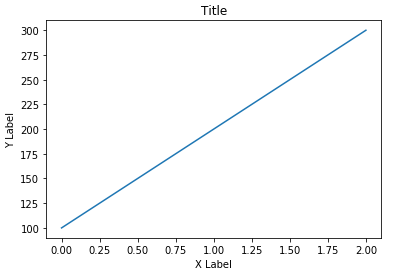
Adding title and name to the axis¶
- we draw the plot
plt.plot(x,y) - we put the title
plt.title('title') - we name the axis
plt.xlabel('X Label'), plt.ylabel('Y Label')
Adding limits or changing the axis scale¶
We can limit or expand the limit of the graphic, in this case we want the previous plot axis to start 0 for X and 100 for Y and finish at 2 for X and 30 for Y.
Changing the markers¶
We can change the color and style of the line, but also we can change the style of the markets
Seaborn¶
Seaborn is a library on top of Matplotlib that allow the creation of different charts and graphics with less code
for the examples we will use a Csv file
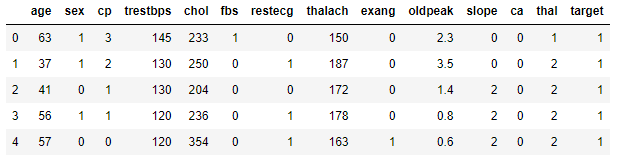
Distribution plots¶
Resizing and modify seaborn plots¶
for resizing
to remove the KDE (Kernel Density Estimates)
similar to remove the histogram
to change the color
we can limit the axis in seaborn as we limit the axis in matplotlib
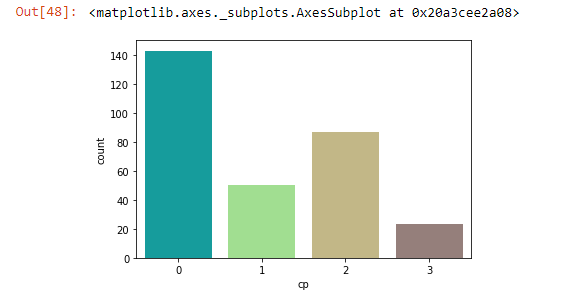
Count plot¶
From the same csv file
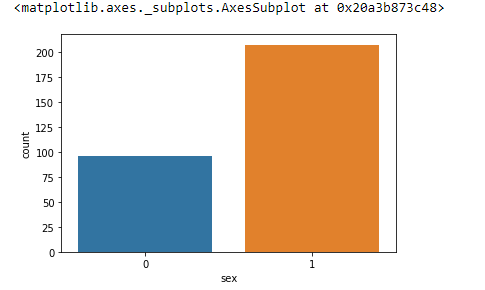
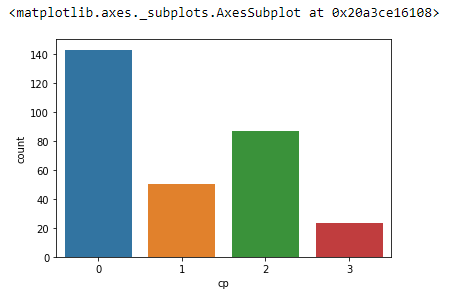
and we can use hue to add more information
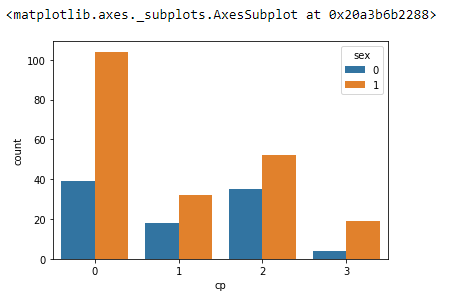
we can change the color ( there are predefine color colormaps)
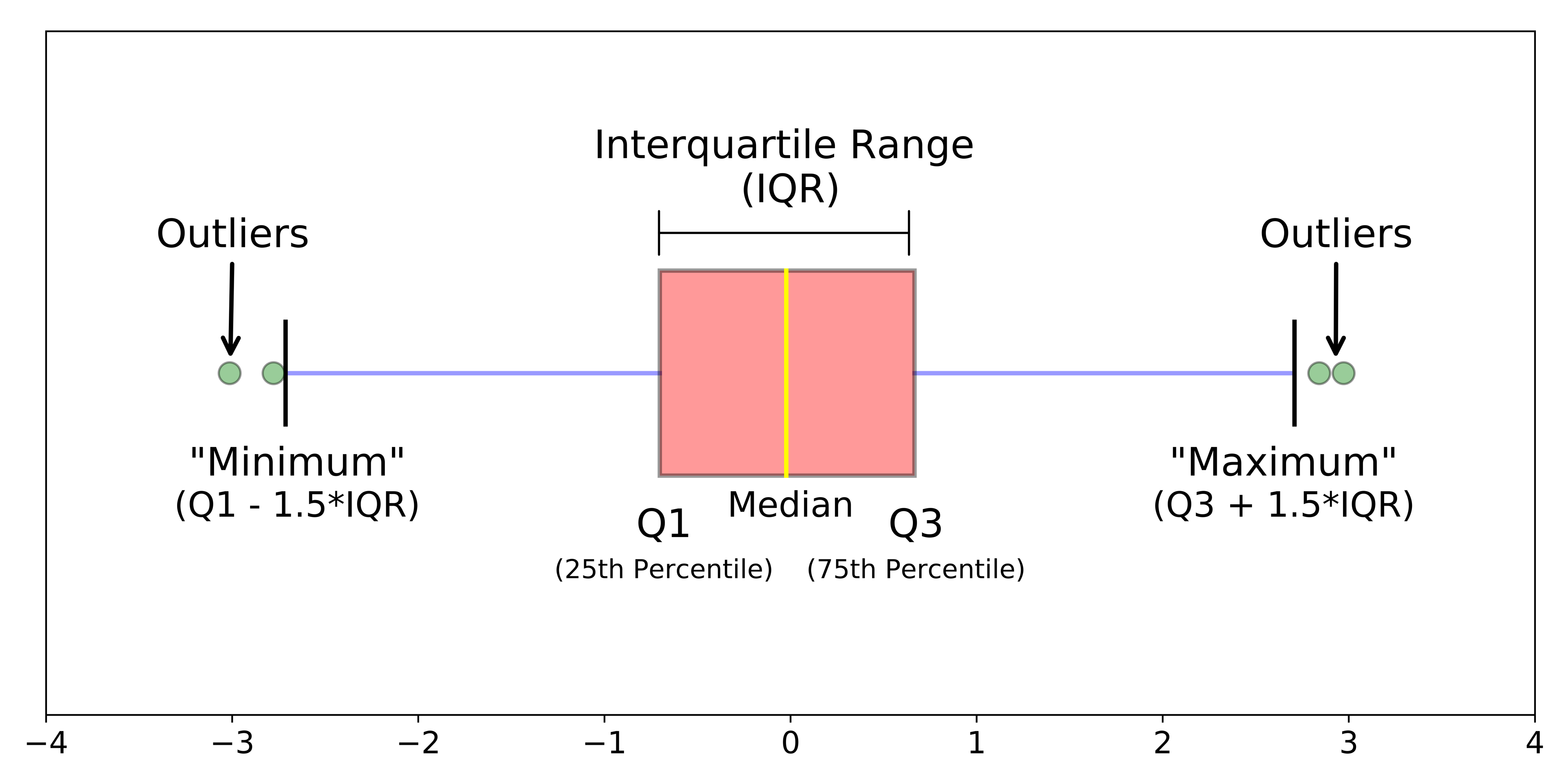
Box Plot¶
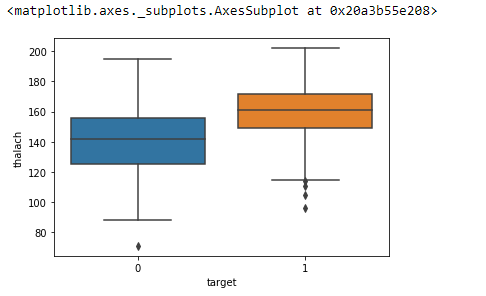
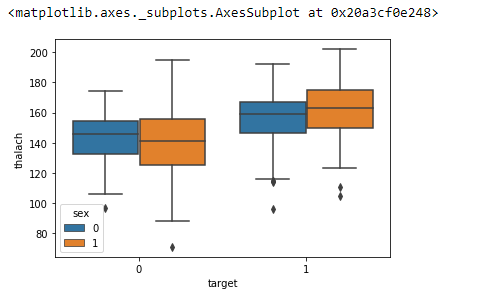
and in the same way that with count plots we can use the hue to add more information to the Box plot
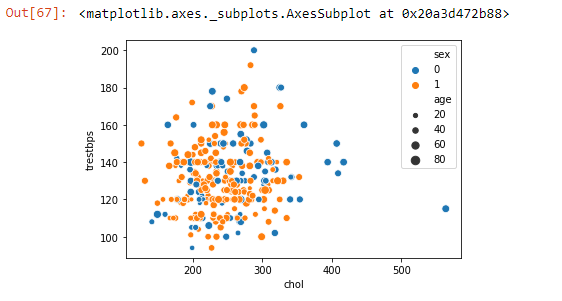
Scatter plot¶
This kind of plot is use to display the relationship between two continuous features
we can use the hue and size to add extra dimension, and use palette to change the color more info
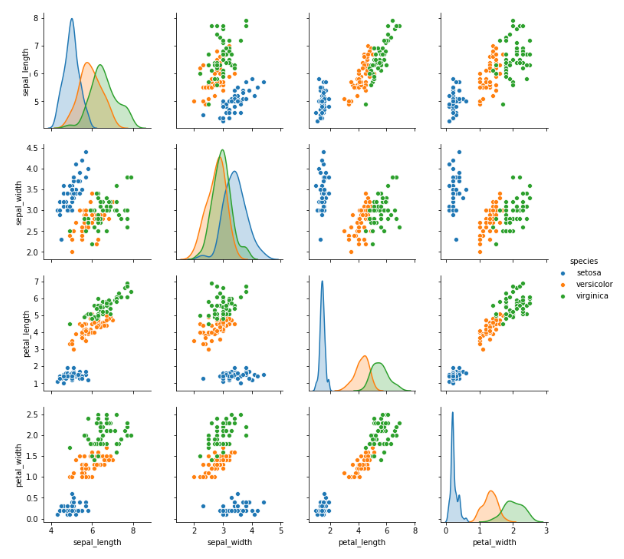
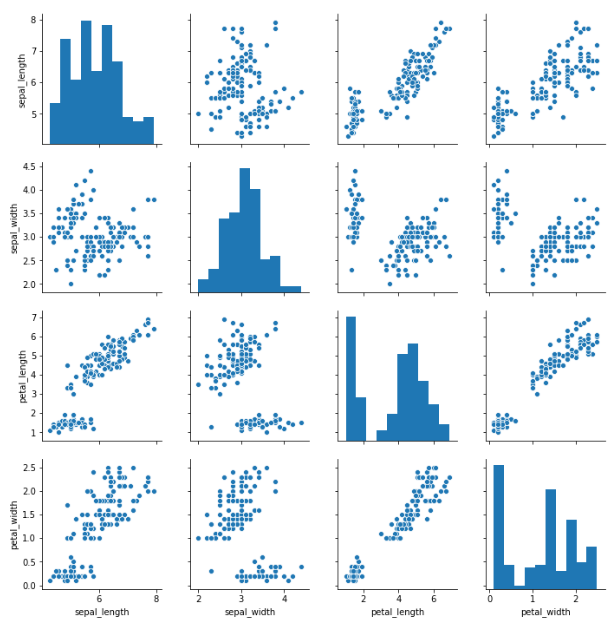
Pairplots¶
Pairplots perform scatterplots and histograms for every single column in your data set. This means it could be a huge plot for large datasets! Use with caution, as it could take a long time for large datasets and the figures could be too small! more info
or just show the KDEs instead of histograms