Functions
Functions on easylanguage are similar to functions in other languages, not in syntax but in concepts, these are use to encapsulate logic to easy debugging and to avoid repetition.
Making a Function¶
to make a function we need to go to File -> New and select function:
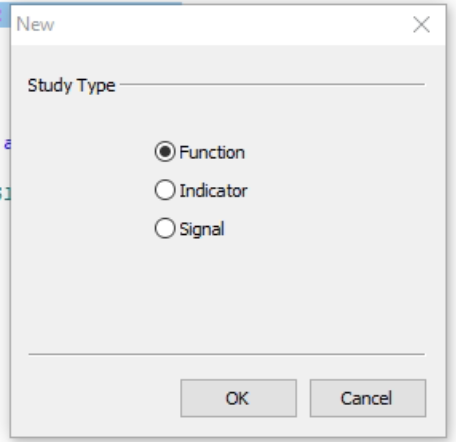
the next screen will display the options for the name of the function, the return type and the function storage
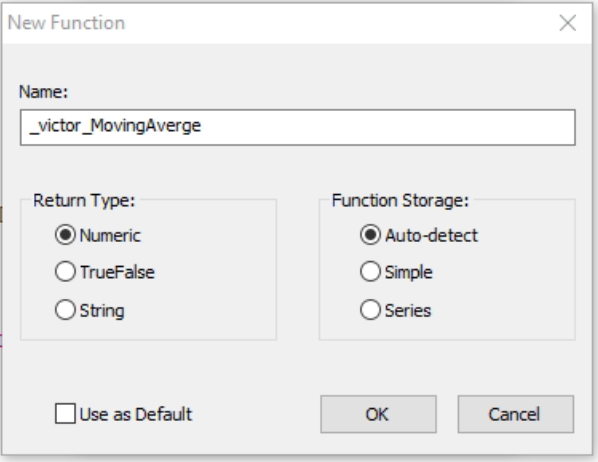
The name¶
like in other languages the function name should be descriptive and not contain special characters with the exception of underscore
The return type¶
the return type like in other languages specify the type of result that the function returns to the caller, if this return is a numeric value we need to select "Numeric", if the function returns a boolean value, we will need to choose "TrueFalse", finally if the function returns string we will choose "String"
The function Storage¶
In this case the best option will be "Auto-detect", the reason is, that we will have lest problems if we decided to make significant changes to the function, the "Simple" it is use when inside the function we don't use previous bar's values, that means we don't use square baskets, if we decide to use square brackets the function storage option to select will be "Series"
Functions Inputs¶
In the indicators you need to specify the default value of the inputs, in the functions code, you have to specify the type of each input, this tell the program what input value to expect while the code is running.
In most of the cases we will work with three type of input parameters:
- Numeric
- TrueFalse
- String
Each of these types have one or two subtypes, series and simple, A simple way to see this will be; If a particular input parameter is constant it is Simple, for example ins a Moving average the length value use to calculate it will be a subtype Simple in other words NumericSimple, but the price, since this change or vary all the time, it will be define as subtype Series, that is why the price input will be NumericSeries.
Function Outputs¶
We can also use Inputs to receive values from the function, these "in&out" inputs can refer values to the caller, in this way we can create a function that not just give a return value, but also a series of values related with he operation, as an example, The stochastic, it return 4 values additional to the return value, this values are; Slow %K, Slow %D, Fast %K and Fast %D.
to declare this reference input, we do it as a regular input with the difference that this will have "Ref" at the end of the type, It is important to mention that the convention in easylanguease is to name this type of reference inputs with a "o" at the beginning of the name, this will give more information and it will be easy to read.
Return Value¶
Each function will need to give a value, even if this is a dummy value, this done assigning the value to return to the name of the function.
We can pass a reference array to and from the function, this is done with NumericArray, NumericArrayRef,TrueFalseArray,TrueFalseArrayRef,StringArray,StringArrayRef.
An Example of a Function¶
We are going to make a function that will calculate the moving average so for that we need
The Inputs¶
the inputs will be the Price and the AverageLenght
The variables¶
the variables to be use in the logic will be
The logic¶
now we use the counter to go through all the values in previous bars ( Averagelength ) all this sum will be store in CloseValueSum and later the Average will be calculated
The return¶
Now we need to store the result in the name of the function so we can use it in an indicator
Using the Function¶
now we can call this function from other indicator, and the code for this indicator will be