Basic Concepts
Throughput vs Bandwidth¶
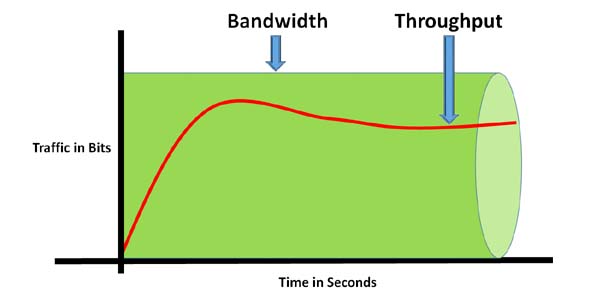
Throughput tells you how much data was transferred from a source at any given time and bandwidth tells how much data could theoretically be transferred from a source at any given time.
Throughput¶
The network throughput refers to how much data can be transferred from source to destination within a frame of time. Throughput measures how many packets arrive at their destinations successfully. Packet loss, latency, and jitter are all related to slow throughput speed. Latency is the amount of time it takes for a packet to make it from source to destination, and jitter refers to the difference in packet delay.
Bandwidth¶
The bandwidth definition will be Network bandwidth is defined as the maximum transfer throughput capacity of a network. It measures how much data can be sent and receive at the same time. It is important to know bandwidth doesn't increase the speed of a network, it just appears to make the network faster.
Let’s say 1 Mbps is the equivalent of a single-lane freeway. Let’s also say you want to download a 5 Mb image. If you had a connection with a bandwidth of 1 Mbps (one lane) it would take you about five seconds to download that image. Now, if you were operating with a 5 Mbps bandwidth connection (five lanes)
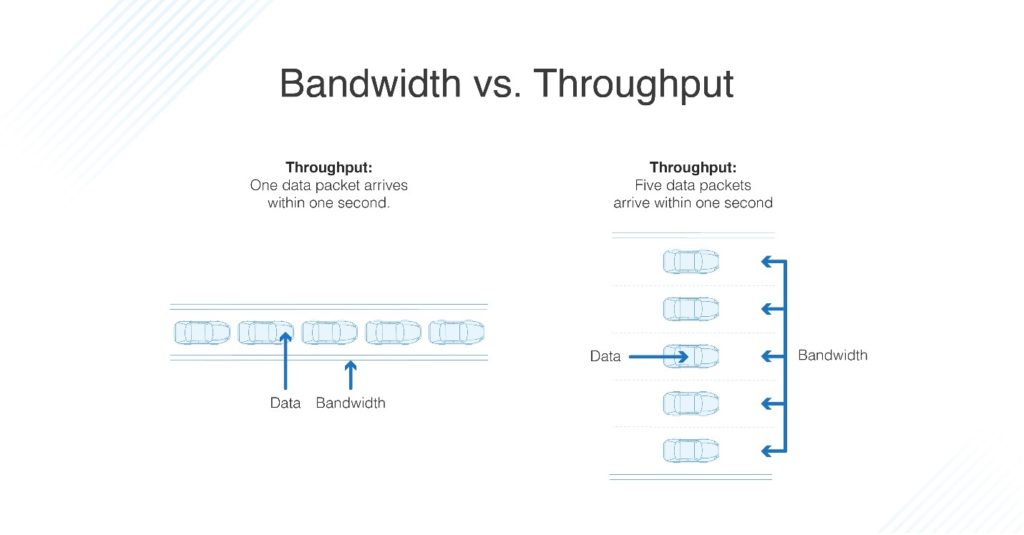
You can think of bandwidth as a tube and data throughput as sand. If you have a large tube, you can pour more sand through it at a faster rate. but, if you try to put a lot of sand through a small tube, it will go very slowly.
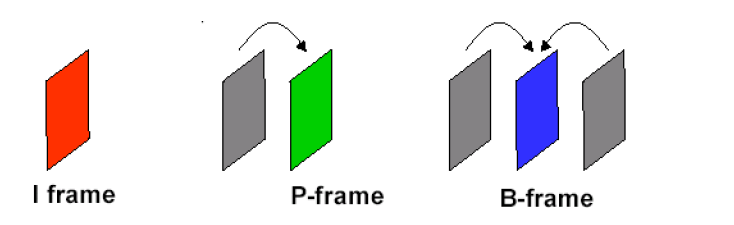
I-P-B Frames¶
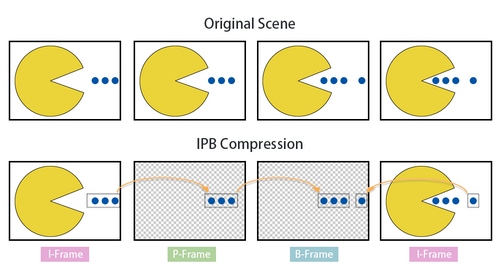
I-FRAME or Intra-coded picture, least compressible of all frames but it doesn't require other frames to be decoded, it is a complete image, similar to .jpg, compress just I-Frames will result in good quality but heavy file.
P-Frame or Predicted picture, more compressible than the I-FRAME, it uses information of the previous frame to decompress. It only holds the part of the image that changes comparing with the last frame.
B-Frame or Bidirectional predicted picture can use both previous and forward Frame to get the highest amount of data compression, use the difference between the current frame and both the preceding and following frame to specify its content.
Video format and codecs¶
Video Formats¶
It is common to find an extension for video files like .mp4 and .avi and is even more common to misunderstand this extension or containers for the codec.
When we talk about mp4 we are not talking about a single file, instead of a container of multiple files. It consists of video files, audio files, and metadata files.
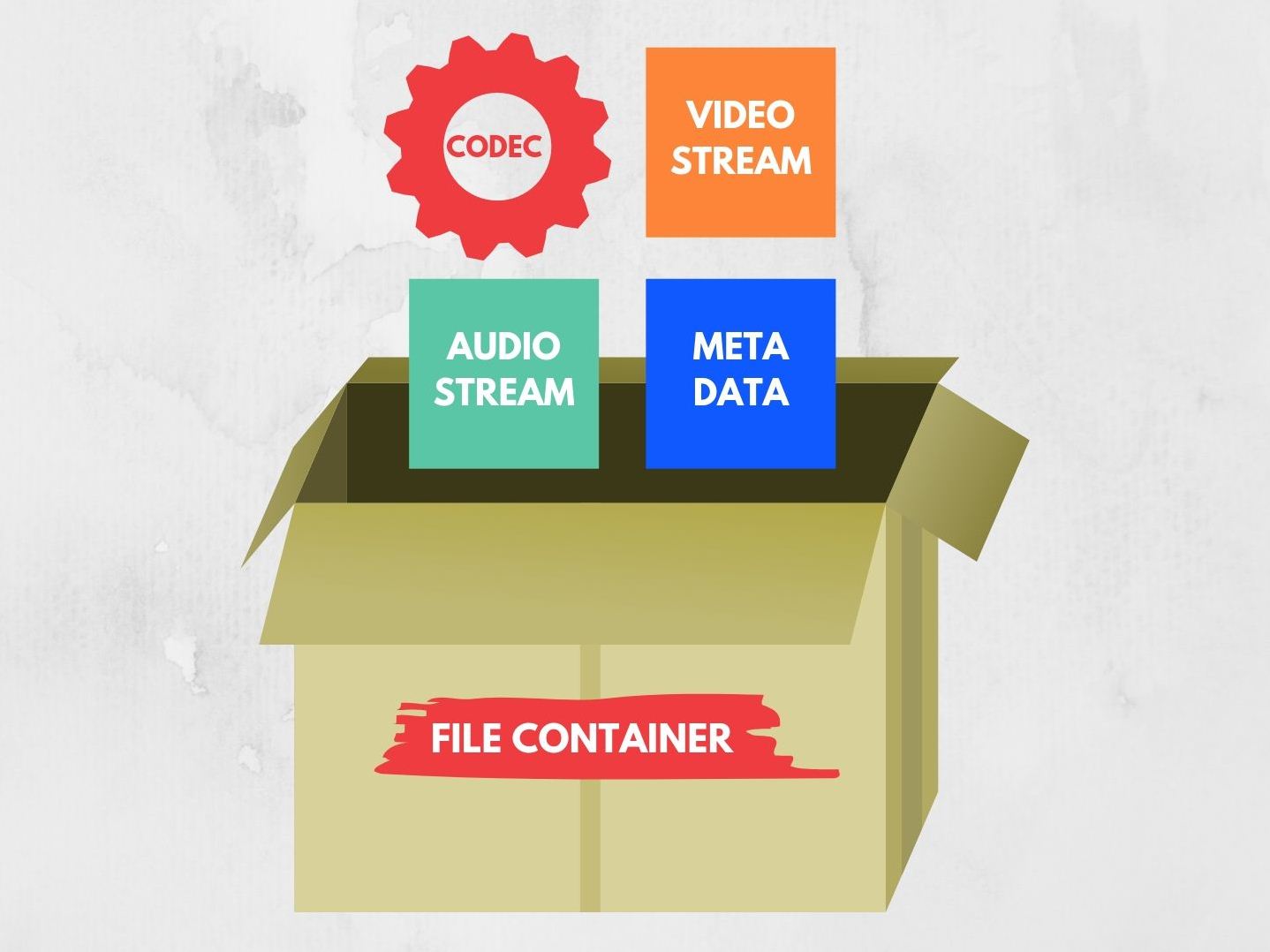
The most common containers for CCTV will be AVI and MP4.
Video Codec¶
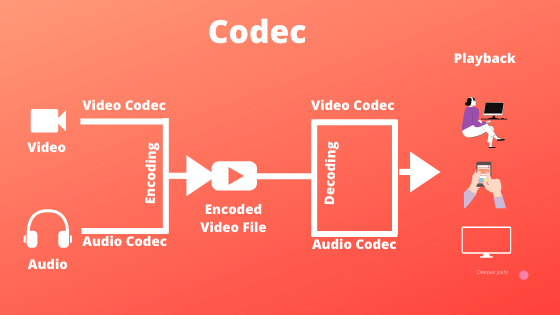
Now the name codec comes from the combination of Coder and decoder $$ Codec = Coder + Decoder $$
We talk about software codec but be aware that the name
codecapplies to hardware as well.
To make the video manageable and smaller, codec creates an encoded stream or a compressed version of the video and the audio, software like VLC player can then decode that video stream and present the result.
It is important to know that most of the codec is "lossy" or "lossy compression", in other words, some quality is lost during the compression.
The most common codec use in CCTV for video are:
"lossless" codec we have MJPEG.